Flutter
Google Flutter is a framework for developing applications for iOS, Android and Web with same code base. It uses Dart as programming language. The dart code gets compiled to java/javascript/swift for native performance. It has rich open source libraries to plug in.
Everything is a widget here :)
Quickstart
flutter create --org com.codeo myappcreate a basic appflutter pub getgets all packagesflutter run -d Chromeruns flutter app on device chromepod setupmakes ios deploy fasterflutter build web/apkbuilds app for publishing
Structure
- assets - hold images/fonts
- lib - all the dart code
- we can make folders specific for activity
- models - hold class for data in the app like users.dart, deserialize json
- pages - hold screens, each .php page or route
- widgets - component on pages, like progress bar
- all folders are packages, eg, lib package, src package, models package.
Basic Workflow
- make product class, init constructor, add factory, the get and set functions
- link this to sqflite
- have a db_provider
- and an init function
- crud functions
- or firebase
- get reference of a collection in instance.
- from ref get the snapshots and build.
Development
add(a,b) => a + bcreates function inline and returns valuel, can be without name.setState(){}- rebuilds the app. usually used in onTap(){}.- wrapping parameters in {} make them named params and we have to specify the name when passing them in call. eg:
emp({String name, Int age}), when called,emp(name: 'Jon', age: 34). initState() {}function gets executed in every State ful widget. can be used to call all what we want to initialize, like db fetch etc.<Future>needs to be handled. Either we can use.then((data) {...})or we can add keywordsasync...awaitto the functions.factorybefore a func declaration makes it accessible outside class just like static.- To preserve state of app, use mixin keep alive.
- await and async are good to wait for a process to finish and the execute the rest.
- Null-aware Operators in Dart
Navigation:
- We can generate route on the go with Navigator.pop or push.
Function calling
- When work needs to be done on call, then pass refrence.
- When function builds/returns then call with ()s.
- Here is the difference:
- onPressed: _incrementCounter is a reference to an existing function is passed. This only works if the parameters of the callback expected by onPressed and _incrementCounter are compatible.
- onPressed: _incrementCounter() _incrementCounter() is executed and the returned result is passed to onPressed. This is a common mistake when done unintentionally when actually the intention was to pass a reference to _incrementCounter instead of calling it.
External Links:
- appicon.co - app icons
- icons8.com - use icons for free
- vecteezy.com - icons
- canva.com - create own design
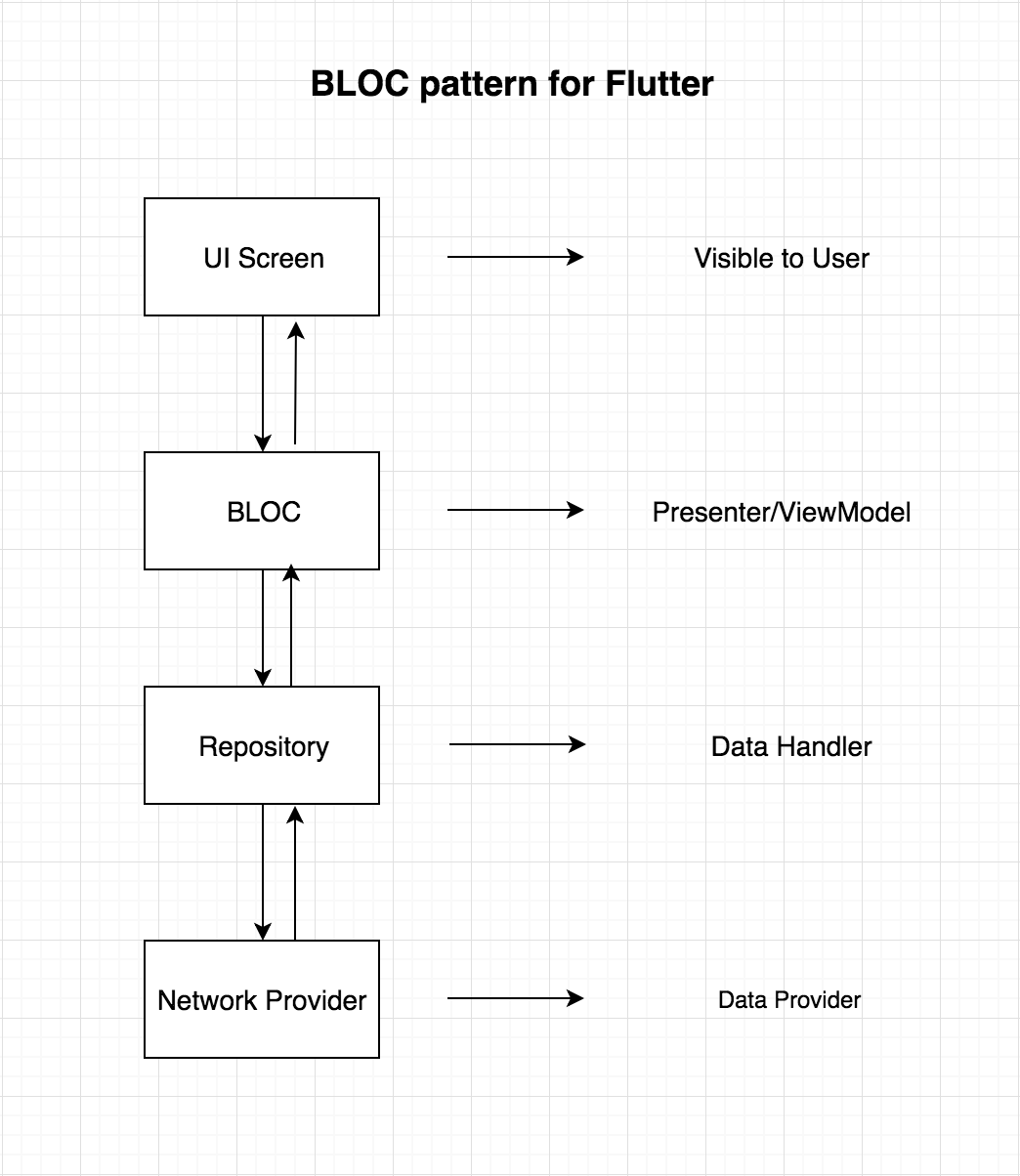
Flutter State Management
Flutter allows to use many kind of state management architectures like Redux, BLoC, MobX and many more. These all are commonly used architecture to layer out UI from Database/WebAPIs.
BLoC - Business Logic Component
- separates UI from Business logic (Database and Network).
Sink<data>- data in - eventsStream<data>- data out - state
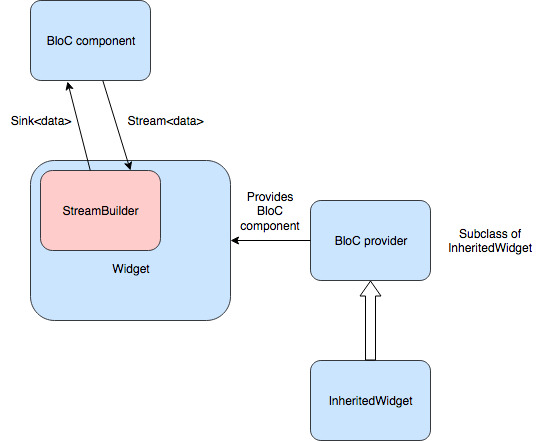

- BLoC component converts a stream of incoming events into a stream of outgoing states.
- Close bloc references in despose() methods.
- It has:
- Bloc
- BlocBuilder
- BlocProvider
- Reactive Programming, whenever there is new data coming from the server. We have to update the UI screen
- KeyNote: never make any network or db call inside the build method and always make sure you dispose or close the open streams.
- Single Instance - all screens have access to bloc, there is one instance in the app
- Scoped Instance - only widget to which the bloc is exposed has access
- PublishSubject: Starts empty and only emits new elements to subscribers. There is a possibility that one or more items may be lost between the time the Subject is created and the observer subscribes to it because PublishSubject starts emitting elements immediately upon creation.
- BehaviorSubject: It needs an initial value and replays it or the latest element to new subscribers. As BehaviorSubject always emits the latest element, you can’t create one without giving a default initial value. BehaviorSubject is helpful for depicting "values over time". For example, an event stream of birthdays is a Subject, but the stream of a person's age would be a BehaviorSubject.
- We pass the blocProvider to MaterialRoute and then it houses all the variables to be passed. This acts as inheritedWidget.
- MovieApp - Part 2
The workflow of the Counter App:
- add packages
- create events as enum.
- create state - in this app, state is
intso we don't create state class. - create bloc to take events, map it, and return state,
class CounterBloc extends Bloc<CounterEvent, int> {...}- here override init state
- and override mapEventsToState
- instantiate bloc in main using
BlocProvider<Bloc>{}. - create Page, get bloc,
- get bloc,
final CounterBloc counterBloc = BlocProvider.of<CounterBloc>(context); - body will be
BlocBuilder<CounterBloc, int>();to build UI based on state. - action event,
onPressed: () {counterBloc.add(CounterEvent.increment);} - based on Flutter Counter App tutorial by @felangel.
Redux:
- provides routing as well
- works with store reducer concept
ScopedModel
- Updates only model in scope, not the whole widget tree
- Have to notifyListeners() on each state change
Links:
Firestore and Flutter
Connecting apps:
- iOS:
- add GoogleService-Info.plist in xCode
- add reverseClientId in key CFBundleURLSchemes Runner/info.plist
- android:
- add google-services.josn and
- make sure applicationId is correct in app/build.gradle
Reading data (Flutter):
- Create a reference to instance of a collection,
userRef = Firestore.instance.collection('users'). - The above has functions to fetch records as snapshot of data
- It returns future which need to be handled.
- use StreamBuilder
- stream: Firestore.instance.collection('users').snapshots(),
- reference object accepts chain of functions like
where()..orderBy()..limit()etc. for compound queries. FutureBuilder- reads data in databaseStreamBuilder- provides stream to data, shows new user added.
NoSQL Structuting:
- do not nest collections
- keep data flatten
- copy data but mostly stored in the way it is best to be fetched.
Create/Update/Delete data (Flutter):
- onTap: () => record.reference.updateData({'key': new_value})
- now its all linked from front to back
- all sync and updates offline and online.
- reference has function like
add()..updateData()..delete(). They all return<Future>.
Triggers:
- user firestore triggers to listen and act on the change in a collection.
- It uses node js to write and deploy the functions.
- Triggers can be created by using Trigger functions. Steps:
firebase login- login to your google account to use CLI.firebase init fucntions- create fucntions folder in flutter project.firebase deploy --only functions- deploy functions to firebase cloud.
References:
- Felix Angelov - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=knMvKPKBzGE
- Brian Egan - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wfc5LMgWaRA
2025-01-12
Jul 2020